Whether it’s due to growing housing demand, rapidly advancing urbanization, natural disasters, or the effects of climate change, the pressure on the construction industry continues to increase. What’s needed are solutions that can be implemented quickly, efficiently, and sustainably. In this context, modular construction is gaining increasing significance: it enables shorter construction times, flexible usage concepts, and a responsible approach to resource management. Thanks to its high degree of prefabrication and standardized components, modular construction offers a promising approach to overcoming current and future challenges in residential construction and beyond.
Building by System: What is modular construction?
The term "modular construction" or "modular building method" is not clearly defined. It is frequently equated with volumetric construction – that is, the building principle in which fully equipped spatial cells are combined as load-bearing units to form a building. This form often visually resembles container solutions, but goes far beyond that.
In reality, however, modular construction encompasses far more than just spatial cells. The term fundamentally describes all construction methods in which buildings do not arise conventionally step by step on the construction site, but rather consist of individual modules that are prefabricated under factory-like conditions and subsequently assembled. This approach follows a systematic structure according to the modular principle – modular, flexible and time-saving. It enables precise processes in planning, manufacturing as well as assembly and thus offers a convincing alternative to classic construction methods.
Basic principles of modular construction
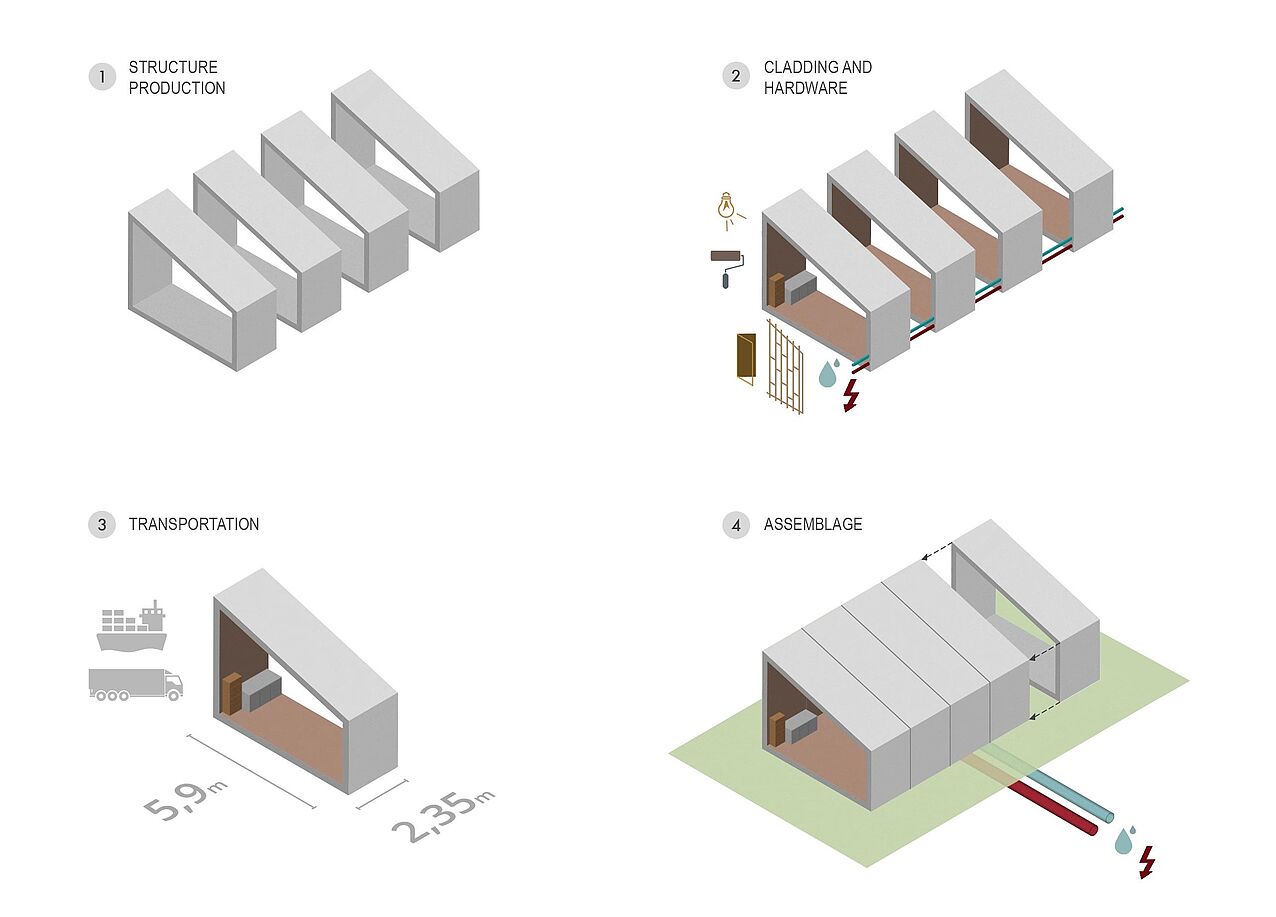
Modular construction follows a clearly structured concept that focuses on efficiency, flexibility, and quality. The entire process is based on four coordinated steps – from the first building component to the finished building unit:
> Structural Fabrication: First, the load-bearing base structure of the modules is produced in the factory. Manufacturing under controlled conditions ensures consistent precision and stability – regardless of weather or site conditions.
> Interior Fit-out and Façade Installation: In the next step, technical systems are installed, façades are mounted, and interior finishing is completed. The result is nearly fully equipped modules with a high standard of workmanship, ready for transport.
> Module Transport: The finished units are delivered to the construction site protected from the weather. Thanks to precise pre-planning, this step reduces logistical uncertainties and shortens on-site processes.
> On-Site Assembly: On the prepared foundation, the modules are quickly and cleanly assembled. The minimal installation effort reduces disruption to the surrounding environment and enables rapid project completion.
Together, these steps enable a highly coordinated construction method that saves time, conserves resources, and ensures consistently high quality – a key contribution to sustainable and cost-effective building.
From Temporary Solution to High-Tech Approach – The Evolution of Modular Construction
What was originally conceived as a quick fix for temporary accommodation has developed into a technically sophisticated construction method with enormous potential. Today, modular construction meets the highest standards in architecture, energy efficiency, and design. Digital tools such as Building Information Modeling (BIM) enable precise coordination between planning, prefabrication, and assembly.
In addition to efficiency and flexibility, ecological considerations are increasingly coming into focus. The shift toward resource-efficient, durable, and adaptable modular buildings is being strongly shaped by current sustainability trends – trends that are playing a key role in defining the future of construction.
Material Diversity in Modular Construction – Overview of Common Module Types
Depending on the area of application, requirements, and architectural concept, different materials are used in modular construction – each type of module comes with specific characteristics and advantages:
| Material | Properties |
| Timber Modules | Lightweight, renewable raw material, good thermal insulation, ideal for sustainable projects |
| Steel Modules | Very robust, high load-bearing capacity, well-suited for temporary or mobile modular buildings |
| Reinforced Concrete Modules | Solid, durable, high sound insulation, ideal for permanent modular construction |
| Hybrid Modules | Combination of materials, flexibly adaptable, balanced in terms of structural performance and sustainability |
However, choosing the right material is only one aspect. To properly understand modular construction, it’s worth taking a closer look at how it differs from other building methods.
Distinguishing Modular Construction from Other Building Methods
Modular construction is often equated with precast construction or serial construction. While all three methods share certain industrial principles, they differ significantly in their degree of prefabrication, planning logic, and on-site effort.
> Precast Construction: Individual components such as floors, walls, or stairs are prefabricated in the factory and assembled on site. Technical installations are usually carried out on site.
> Serial Construction: This approach focuses on standardized designs and repeatable processes. The level of prefabrication is lower, and many trades are still executed traditionally on the construction site.
> Modular Construction: Entire room units – often including interior finishes and building services – are produced in the factory and delivered nearly turnkey. This significantly shortens construction time and reduces on-site effort.
Modular construction thus combines a high degree of prefabrication with architectural flexibility and an efficient building process. It represents an independent and particularly high-performance form of industrial construction.
Key Advantages of Modular Building Concepts at a Glance
Modular construction stands out for its efficiency, predictability, and sustainability. In an era of rising demands for faster building times, resource conservation, and economic action, it presents a future-ready alternative to conventional construction methods. The key advantages are summarized below:
> Time and Cost Efficiency: Parallel processes in manufacturing and site preparation significantly reduce overall construction time. The industrial serial production of identical modules enables cost savings and a high degree of schedule and budget reliability. The minimal effort required for on-site assembly further reduces labor and logistics costs.
> Sustainability and Resource Conservation: Precise planning and automated processes ensure minimal waste and lower energy consumption. Production waste is disposed of in a controlled manner, and noise and emissions at the construction site remain low. Many modules can be reused after dismantling – contributing to the circular economy.
> Mobility and Flexibility: Modular buildings can be expanded, modified, or entirely relocated. This makes them suitable for temporary use, hard-to-reach locations, or changing requirements. Even in situations with urgent space needs – such as crisis scenarios – modular solutions offer fast, high-quality results.
These advantages clearly show why modular construction is being used in an increasing number of sectors – from residential buildings to schools and offices, and even complex infrastructure projects. What always matters most is the combination of technical precision, economic efficiency, and design flexibility.

Challenges and Disadvantages of Modular Construction
Despite its efficiency, modular construction also comes with challenges. Especially in planning, in meeting individual requirements, and within legal frameworks, modular concepts are not easily comparable to traditional construction methods. Additionally, the economic advantages are mainly realized with larger quantities – not with one-off solutions.
Design Limitations and Planning Effort
Standardization enables efficiency but reduces architectural design freedom. Therefore, custom floor plans or special design solutions require additional planning. To ensure that all modules fit together perfectly on site, a high level of detail is necessary – usually based on digital tools such as CAD.
As a result, the time and cost advantages are less pronounced in single projects. In the future, the growing use of 3D printing could help integrate custom solutions more economically into modular processes.
Legal Framework for Modular Construction
Modular buildings are subject to the same legal requirements as conventional structures. However, specific aspects arise due to prefabrication and modular workflows. Here is an overview of the most important considerations:
> Inspections in the Factory Instead of On-Site: Many modules already include load-bearing elements, technical installations, or fire protection systems. As a result, certain inspections must take place in the factory rather than on the construction site – requiring separate coordination with inspection authorities.
> Varying Classifications Depending on the Federal State: Depending on the project and region, a module may be classified either as a construction product or as part of an overall building. This legal classification affects the approval process and may lead to additional coordination efforts in cross-state projects.
> Special Regulations for Temporary Use: Mobile daycare centers, modular school buildings, or temporary accommodations are often subject to different rules – for example regarding approval periods, permitted usage duration, or dismantling obligations.
> Legal Issues Around Smart Building Technology: Pre-installed sensors, control systems, or connected building technology require not only technical but also data protection compliance.
Early, project-specific coordination with the relevant authorities is therefore essential to ensure legal requirements are met accurately and to avoid delays in the approval process.
From Housing to Daycare – Application Areas for Modular Building Concepts
Modular buildings are used in a wide range of sectors – wherever speed, efficiency, and adaptability are required. Three areas of application clearly demonstrate the potential of modular construction:
> Residential Construction: In urban areas, modular construction helps create housing quickly and cost-effectively. Thanks to short construction times and flexible floor plans, a wide variety of housing types can be realized – from micro-apartments to family homes. Modular housing is also a proven solution for densification projects or temporary accommodation, as the units are compact, quickly deployable, and can be dismantled if needed.
> Commercial and Office Buildings: Businesses benefit from flexible space solutions that can be expanded or adapted to new ways of working as needed. Modular office buildings offer high-quality fit-outs, short planning phases, and can be implemented independently of location.
> Public Buildings: For municipalities, modular schools, daycare centers, or clinics provide a fast and cost-efficient response to growing demand. These buildings are expandable, energy-efficient, and can be easily repurposed or dismantled as needs change.
Modular construction proves across all sectors that building quickly doesn’t have to come at the expense of quality or functionality. Given increasing space demands, demographic shifts, and changes in the world of work, its share of total construction volume is set to grow.
Practical Examples Where Modular Buildings Have Already Been Implemented
Theory and planning demonstrate the potential of modular construction – but it’s the completed projects that make its capabilities tangible. Whether for housing, emergency shelters, or urban infill, modular buildings prove their worth in practice through speed, adaptability, and construction quality. The following examples illustrate how versatile modular construction already is, even under widely varying conditions.
Modular Construction in Berlin-Lichtenberg: Europe’s Largest Project
Europe’s largest modular housing project is currently underway in Berlin-Lichtenberg. By 2026, around 1,550 apartments will have been built on the site – mostly prefabricated in a factory and assembled on site. The construction progress is impressive: one complete floor with 36 residential units is completed each week.
Roughly every 30 minutes, a module is precisely installed. The project shows how modular construction on a large scale can help deliver urgently needed housing quickly and sustainably – with precise planning and cost-effective execution.
Disaster Relief in the Ahr Valley: Rapid Response with Modular Construction
After the devastating floods in July 2021, modular housing complexes were quickly built in the Ahr Valley to provide safe shelter for those affected. The prefabricated units included not only private living spaces but also essential infrastructure such as sanitary facilities and communal areas.
The Workers’ Samaritan Federation (ASB) implemented several of these complexes, demonstrating how modular construction can serve as a flexible and immediately deployable solution in crisis situations. This example highlights the potential of modular building for rapid relief and organized reconstruction under extreme conditions.
Modular Rooftop Extension in Frankfurt: New Housing Without New Builds
In Frankfurt, Nassauische Heimstätte expanded several residential buildings by adding modular rooftop extensions using timber construction. Instead of developing new land, prefabricated modules were placed directly onto the roofs of existing buildings. This meant no additional land had to be sealed – no new surfaces were lost to construction or paving.
In total, 82 new apartments were created without burdening the surrounding area. Construction was completed quickly and during ongoing occupancy, with minimal disruption to the existing residential environment.
Snooze Campus in Koblenz: Temporary Modular Living
In Koblenz, the Snooze Campus project implemented a temporary housing concept consisting of 36 fully equipped single apartments. These were built using container construction, with the modules arranged across three stories. The apartments offer living spaces between 21 and 28 square meters and are characterized by high functionality within a compact footprint – ideal for flexible interim use, with short construction times and low logistical effort.
Technological Innovations in Modular Construction
As digitalization and automation advance, modular construction is evolving rapidly. New technologies are enabling more precise workflows, greater efficiency, and increased sustainability – from planning through to assembly. Three key developments are driving this transformation:
> Robotics in Production: In modern manufacturing facilities, robots handle tasks such as cutting, assembly, and the installation of technical systems. This improves execution quality, reduces the risk of errors, and shortens production time – enabling standardized processes in modular construction.
> Automated Manufacturing and Digital Planning: Digital production lines, combined with Building Information Modeling (BIM), enable end-to-end control from planning to logistics to delivery. This makes material use and construction processes highly predictable – transparent, efficient, and resource-conscious.
> 3D Printing for Custom Components: 3D printing is becoming increasingly relevant in the construction industry. Initial projects show that complex or custom components can be produced automatically – and potentially entire modules in the future. This allows for greater design freedom while maintaining a high level of prefabrication.
These technologies are opening new possibilities for the future of modular construction – precise, scalable, and environmentally sound. The combination of standardized processes and digital flexibility makes modular construction even more capable and future-ready.
The Future of Building: Why Modular Construction Is So Compelling
Whether in residential construction, public facilities, or commercial buildings, modular construction offers fast, flexible, and sustainable solutions to the challenges facing the construction industry. Short construction times, precise planning, cost certainty, and low environmental impact make it a future-ready alternative to traditional building methods.
Technological innovations such as automated manufacturing and digital planning further enhance its potential. In light of growing demands for efficiency and sustainability, modular construction will continue to gain importance. Anyone involved in planning buildings should actively consider this method as a key to modern, responsible construction projects.




